Brief Neuropsychological Cognitive Examination Pdf Editor
Posted on -
University Of Brescia

- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:189–98.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shulman KI, Herrmann N, Brodaty H, et al. IPA survey of brief cognitive screening instruments. Int Psychogeriatr. 2006;18:281–94.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Han L, Cole M, Bellavance F, McCusker J, Primeau F. Tracking cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease using the mini-mental state examination: a meta-analysis. Int Psychogeriatr. 2000;12:231–47.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diniz BS, Yassuda MS, Nunes PV, Radanovic M, Forlenza OV. Mini-mental State Examination performance in mild cognitive impairment subtypes. Int Psychogeriatr. 2007;19:647–56.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Toglia J, Fitzgerald KA, O’Dell MW, Mastrogiovanni AR, Lin CD. The Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal Cognitive Assessment in persons with mild subacute stroke: relationship to functional outcome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;92:792–8.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mystakidou K, Tsilika E, Parpa E, Galanos A, Vlahos L. Brief cognitive assessment of cancer patients: evaluation of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) psychometric properties. Psychooncology. 2007;16:352–7.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jones RN, Gallo JJ. Dimensions of the Mini-Mental State Examination among community dwelling older adults. Psychol Med. 2000;30:605–18.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schultz-Larsen K, Kreiner S, Lomholt RK. Mini-Mental Status Examination: mixed Rasch model item analysis derived two different cognitive dimensions of the MMSE. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:268–79.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Crews Jr WD, Harrison DW, Keiser AM, Kunze CM. The memory screening outreach program: findings from a large community-based sample of middle-aged and older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57:1697–703.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lazaro L, Marcos T, Pujol J, Valdes M. Cognitive assessment and diagnosis of dementia by CAMDEX in elderly general-hospital inpatients. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1995;10:603–9.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, Folstein MF. Population-based norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by age and educational level. JAMA. 1993;269:2386–91.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holzer CE, Tischler GL, Leaf PJ, Myers JK. An epidemiologic assessment of cognitive impairment in a community population. Res Commun Ment Health. 1984;4:3–32.Google Scholar
- Tombaugh TN, McIntyre NJ. The mini-mental state examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992;40:922–35.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, et al. Population-based norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by age and education level. J Occup Med. 1994;36:13–4.Google Scholar
- Grigoletto F, Zappala G, Anderson DW, Lebowitz BD. Norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination in a healthy population. Neurology. 1999;53:315–20.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mossello E, Boncinelli M. Mini-mental state examination: a 30-year story. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2006;18:271–3.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- O’Connor DW, Pollitt PA, Hyde JB, Fellows JL, Miller ND, Brook CP, et al. The reliability and validity of the Mini-Mental State in a British community survey. J Psychiatr Res. 1989;23:87–96.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell AJ. A meta-analysis of the accuracy of the mini-mental state examination in the detection of dementia and mild cognitive impairment. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43:411–31.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell AJ. The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE): an update on its diagnostic validity for cognitive disorders. In: Larner AJ, editor. Cognitive screening instruments. A practical approach. London: Springer; 2013. p. 15–46.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Tsoi KK, Chan JY, Hirai HW, Wong SY, Kwok TC. Cognitive tests to detect dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175:1450–8.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell AJ, Meader N, Pentzek M. Clinical recognition of dementia and cognitive impairment in primary care: a meta-analysis of physician accuracy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2011;124:165–83.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heinik J, Solomesh I, Bleich A, et al. Are the clock-drawing test and the MMSE combined interchangeable with CAMCOG as a dementia evaluation instrument in a specialized outpatient setting? J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2003;16:74–9.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meulen EF, Schmand B, van Campen JP, et al. The seven minute screen: a neurocognitive screening test highly sensitive to various types of dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75:700–5.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Yoshida H, Terada S, Honda H, Ata T, Takeda N, Kishimoto Y, Oshima E, Ishihara T, Kuroda S. Validation of Addenbrooke’s cognitive examination for detecting early dementia in a Japanese population. Psychiatry Res. 2011;185:211–4.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kalbe E, Kessler J, Calabrese P, Smith R, Passmore AP, Brand M, Bullock R. DemTect: a new, sensitive cognitive screening test to support the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and early dementia. IntJ Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004;19:136–43.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Kilada S, Gamaldo A, Grant EA, et al. Brief screening tests for the diagnosis of dementia: comparison with the mini-mental state exam. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2005;19:8–16.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grober E, Hall C, Lipton RB, Teresi JA. Primary care screen for early dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:206–13.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004;256:183–94.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, et al. Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med. 2004;256:240–6.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, et al. Aging, memory, and mild cognitive impairment. Int Psychogeriatr. 1997;9(Suppl1):65–9.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993;43:2412–4.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spering CC, Hobson V, Lucas JA, Menon CV, Hall JR, O’Bryant SE. Diagnostic accuracy of the MMSE in detecting probable and possible Alzheimer’s disease in ethnically diverse highly educated individuals: an analysis of the NACC database. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67:890–6.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Inouye S, Rushing J, Foreman M, Palmer R, Pompei P. Does delirium contribute to poor hospital outcomes? A three-site epidemiologic study. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13:234–42.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Cole M, Primeau F. Prognosis of delirium in elderly hospital patients. CMAJ. 1993;149:41–6.PubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Shi Q, Presutti R, Selchen D, Saposnik G. Delirium in acute stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2012;43:645–9.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Young J, Leentjens AF, George J, Olofsson B, Gustafson Y. Systematic approaches to the prevention and management of patients with delirium. J Psychosom Res. 2008;65:267–72.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wong CL, Holroyd-Leduc J, Simel DL, Straus SE. Does this patient have delirium? Value of bedside instruments. JAMA. 2010;304:779–86.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mitchell AJ, Shukla D, Ajumal HA, Stubbs B, Tahir TA. The Mini-Mental State Examination as a diagnostic and screening test for delirium: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2014;36:627–33.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vertesi A, Lever JA, Molloy D, et al. Standardized Mini-Mental State Examination. Use and interpretation. Can Fam Physician. 2001;47:2018–23.PubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Schultz-Larsen K, Lomholt R, Kreiner S. Mini-Mental Status Examination: a short form of MMSE was as accurate as the original MMSE in predicting dementia. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:260–7.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simard M. The Mini-Mental State Examination: strengths and weaknesses of a clinical instrument. Can Alzheimer Dis Rev. 1998;1(3):10–2.Google Scholar
- Bravo G, Hébert R. Age- and education-specific reference values for the Mini-Mental and Modified Mini-Mental State Examinations derived from a non-demented elderly population. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;12:1008–18.3.0.CO%3B2-A'>CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kahle-Wrobleski K, Corrada MM, Li B, Kawas CH. Sensitivity and specificity of the Mini-Mental State Examination for identifying dementia in the oldest-old: the 90+ Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55:284–9.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Glasser M. Alzheimer’s disease and dementing disorders: practices and experiences of rural physicians. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Dement. 1993;8:28–35.Google Scholar
- Brodaty H, Howarth GC, Mant A, et al. General practice and dementia. A national survey of Australian GPs. Med J Aust. 1994;160:10–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boustani M, Callahan CM, Unverzagt FW. Implementing a screening and diagnosis program for dementia in primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2005;20:572–7.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- McCarten JR, Anderson P, Kuskowski MA, McPherson SE, Borson S, Dysken MW. Finding dementia in primary care: the results of a clinical demonstration project. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:210–7.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cole MG, McCusker J, Bellavance F, Primeau FJ, Bailey RF, Bonnycastle MJ, Laplante J. Systematic detection and multidisciplinary care of delirium in older medical inpatients: a randomized trial. CMAJ. 2002;167:753–9.PubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Marcantonio ER, Bergmann MA, Kiely DK, Orav EJ, Jones RN. Randomized trial of a delirium abatement program for postacute skilled nursing facilities. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:1019–26.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar
- Van Hout H, Teunisse S, Derix M, Poels P, Kuin Y, Vernooij-Dassen M, Grol R, Hoefnagels W. CAMDEX, can it be more efficient? Observational study on the contribution of four screening measures to the diagnosis of dementia by a memory clinic team. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;16:64–9.3.0.CO%3B2-4'>CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fowler NR, Morrow L, Chiappetta L, Snitz B, Huber K, Rodriguez E, Saxton J. Cognitive testing in older primary care patients: a cluster-randomized trial. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2015;1:349–57.Google Scholar
- Pittam G, Allaby M. Screening for dementia: can screening bring benefits to those with unrecognised dementia, their carers and society? An appraisal against UKNSC criteria. A report for the UK National Screening Committee. Oxford: Solutions for Public Health (SPH); 2015.Google Scholar
- Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Recommendations on screening for cognitive impairment in older adults. CMAJ. 2016;188:37–46.CrossRefPubMedCentralGoogle Scholar

Tomaso Bottio
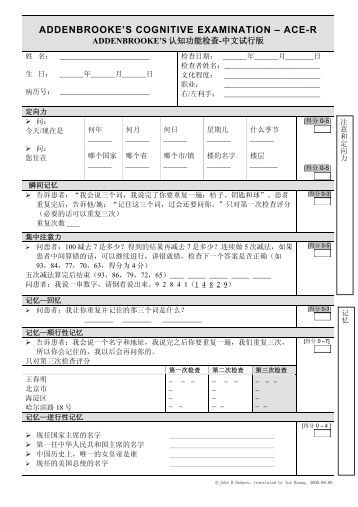
The neuropsychological test battery included administration of the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) (Folstein, Folstein, & McHugh, 1975), the Brief Neuropsychology Cognitive Evaluation (BNCE) (Tonkonogy, 1997), and The Neurobehavioural Cognitive Status Examination (Cognistat) (1985). Awarded a Medal of Achievement for serving as editor-in-chief of School Psychol-ogy Quarterly, the American Psychological Association. Basis of the Neurological Examination 60 General Physical Examination 61 The Neurological Examination 63. 10 Brief and Comprehensive Neuropsychological Assessment of Children and Adults With. Brief neuropsychological exam to help assess cognitive functions in adults, useful with both psychiatric and medical patients.